The Legacy of Great Zimbabwe: Echoes of an African Empire

Hidden in the southeastern hills of Zimbabwe lies one of Africa’s most remarkable archaeological wonders: Great Zimbabwe. Once the center of a vast and wealthy kingdom, Great Zimbabwe stands as a testament to the architectural prowess, economic power, and cultural sophistication of early African civilizations. This ancient city, built entirely of stone without mortar, continues to fascinate historians, archaeologists, and travelers alike.
In this blog post, we explore the legacy of Great Zimbabwe, shedding light on its historical significance, unique architecture, cultural impact, and how it continues to influence Zimbabwean identity today. Whether you're a history enthusiast, a traveler, or a student, this comprehensive guide offers an in-depth look into one of Africa’s greatest empires.
What Was Great Zimbabwe?
Great Zimbabwe was the capital of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe during the Late Iron Age. Constructed between the 11th and 15th centuries, it served as the political and economic center of a powerful empire that controlled large swaths of southeastern Africa. The word "Zimbabwe" is derived from the Shona phrase "Dzimba dza mabwe," meaning "houses of stone."
At its peak, the city may have housed up to 20,000 people. It played a vital role in regional trade, linking the African interior to the Indian Ocean coast. Goods such as gold, ivory, and iron were traded with merchants from Arabia, Persia, and even China.
The Architecture of Great Zimbabwe
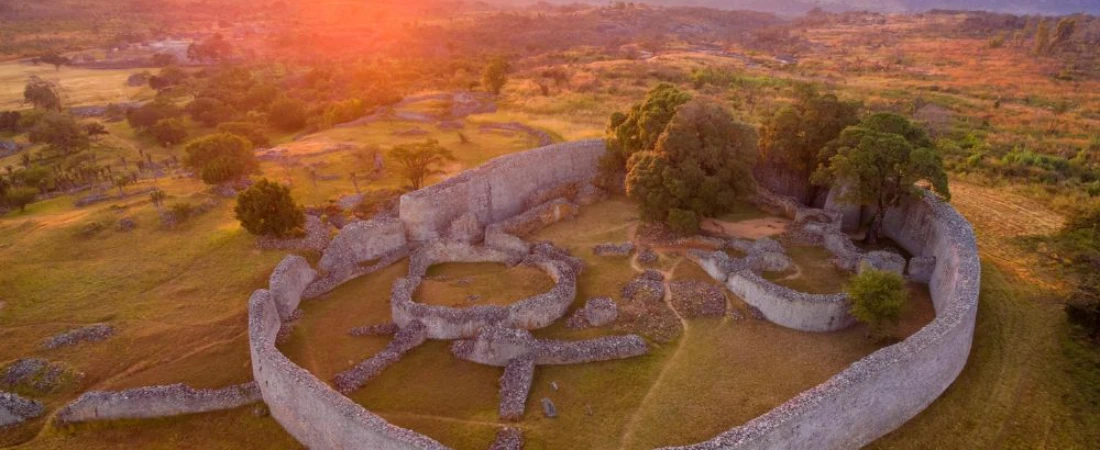

One of the most fascinating aspects of Great Zimbabwe is its architecture. The structures were built using granite blocks without the use of mortar, a technique known as dry stone walling. The walls, some standing over 11 meters high, demonstrate a remarkable understanding of engineering and aesthetics.
Key Architectural Features
- The Hill Complex: The oldest part of the city, believed to have served religious and political purposes.
- The Great Enclosure: The largest ancient structure south of the Sahara, believed to have been a royal residence or ceremonial center.
- The Valley Ruins: Consisting of smaller homes and enclosures, likely housing the general population and craft workers.
The architecture of Great Zimbabwe showcases not only skill but also a deep connection to local materials and environmental conditions, making it an enduring symbol of African ingenuity.
The Rise and Fall of a Great Empire
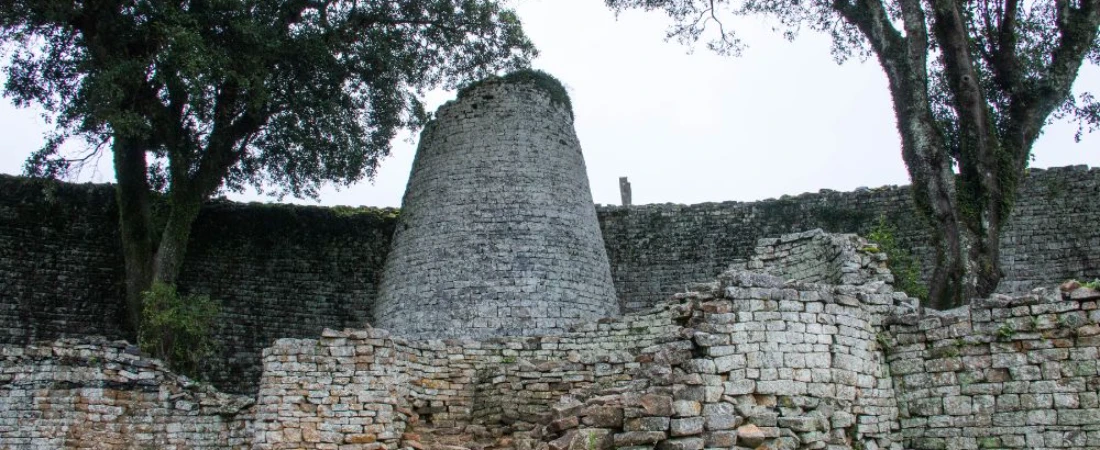

The rise of Great Zimbabwe is closely linked to its strategic location and access to resources. Situated near rich gold mines and fertile land, the city thrived as a center of trade and agriculture.
Factors Behind Its Rise:
- Trade: Participation in the Indian Ocean trade network brought wealth and exotic goods.
- Agriculture: Fertile soils supported large populations.
- Iron and Gold Mining: Provided materials for tools, weapons, and trade.
However, by the 15th century, Great Zimbabwe began to decline. Several theories explain this, including:
- Resource Depletion: Overgrazing and deforestation may have made the area unsustainable.
- Political Fragmentation: Internal conflicts could have weakened central authority.
- Shifting Trade Routes: Changes in trade dynamics reduced the city's economic importance.
The abandonment of Great Zimbabwe led to the rise of new centers of power, like the Mutapa Empire.
Cultural and Historical Significance
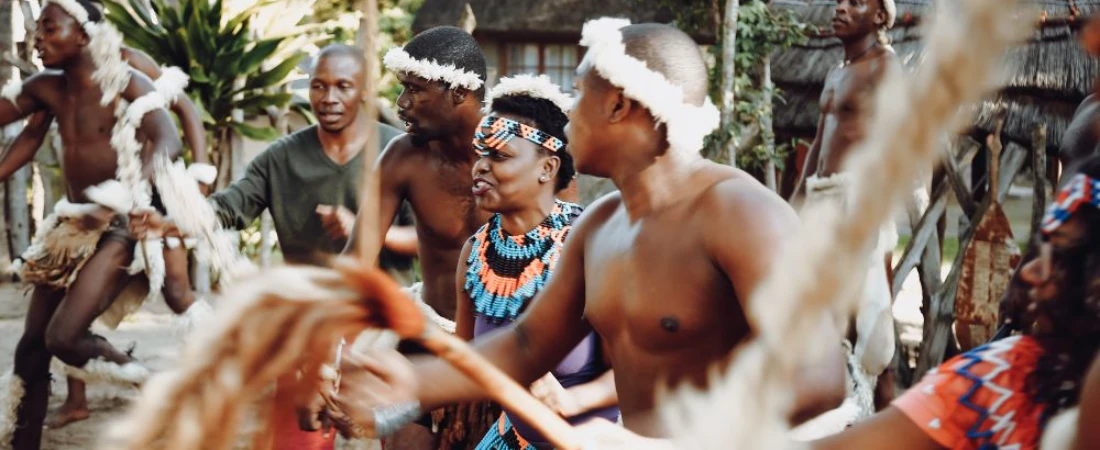

Great Zimbabwe is more than just ruins; it is a cultural touchstone and a powerful symbol of African achievement. For centuries, colonial narratives downplayed or outright denied that Africans could have constructed such a complex city.
A Symbol of National Pride
After gaining independence in 1980, the country adopted the name "Zimbabwe" to honor this heritage. The iconic bird sculptures found in the ruins now feature prominently on the national flag and currency.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
In 1986, Great Zimbabwe was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognizing its global importance. This designation has helped attract international interest and support for conservation efforts.
For more on UNESCO World Heritage Sites, visit UNESCO's official site.
Lessons from Great Zimbabwe

The story of Great Zimbabwe offers several valuable lessons:
1. Sustainability is Key
The decline due to environmental degradation serves as a cautionary tale about the need for sustainable resource management.
2. Cultural Identity Matters
Reclaiming African history from colonial misrepresentation is essential for fostering national pride and unity.
3. Innovation Through Tradition
The use of dry stone architecture shows how traditional methods can be both functional and beautiful.
Visiting Great Zimbabwe Today

Great Zimbabwe is a must-visit destination for those interested in African history and heritage tourism. The site is located near the town of Masvingo and is accessible by road. Guided tours are available, offering insights into the site's history and significance.
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: May to October (dry season)
- What to Bring: Comfortable shoes, sunscreen, water, and a camera
- Nearby Attractions: Lake Mutirikwi, Kyle Recreational Park
For Zimbabwe travel planning, check out Zimbabwe Tourism Authority.
How Great Zimbabwe Influences Modern Culture

Today, the legacy of Great Zimbabwe is evident in various aspects of Zimbabwean culture:
- Education: Schools include Great Zimbabwe in history curricula.
- Art and Literature: Numerous works celebrate the site’s significance.
- Political Discourse: Leaders invoke its legacy to inspire national unity.
Additionally, local artisans continue traditional crafts inspired by the designs and motifs found at the site.
Conclusion
Great Zimbabwe stands as a powerful symbol of Africa’s rich and complex history. Its towering stone walls, intricate architecture, and role in early trade networks speak volumes about the capabilities of African societies long before colonial contact. The city’s legacy lives on in modern Zimbabwean identity, national symbols, and global recognition.
By understanding and honoring sites like Great Zimbabwe, we not only preserve the past but also inspire future generations to value cultural heritage and sustainability. Whether you're exploring it through research or planning a visit, Great Zimbabwe offers a profound glimpse into the heart of a forgotten empire that still echoes through time.